Kaizen, a Japanese term meaning “change for better,” is a philosophy that originated in Japan after World War II. Introduced by management guru Masaaki Imai, Kaizen focuses on continuous improvement in all aspects of life, emphasizing incremental changes for enhanced efficiency and effectiveness.
Components of Kaizen:
- Continuous Improvement: Kaizen promotes a culture of constant, small improvements rather than sporadic, large changes.
- Employee Involvement: All employees, from top management to frontline workers, actively contribute to identifying and implementing improvements.
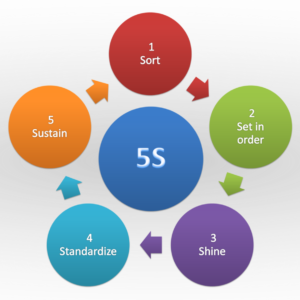
- Standardization: Developing and adhering to standardized processes ensures consistency and facilitates ongoing enhancements.
- Elimination of Waste: Kaizen targets waste reduction, be it in time, resources, or materials, aligning with lean principles.
- Empowerment: Employees are empowered to suggest and implement improvements, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability.
Benefits of Kaizen:
- Increased Efficiency: Continuous improvements lead to streamlined processes and increased productivity.
- Cost Reduction: Identifying and eliminating waste reduces operational costs.
- Employee Morale: Involving employees in decision-making boosts morale and job satisfaction.
- Enhanced Quality: Continuous improvement often results in higher-quality products or services.
- Adaptability: Kaizen encourages adaptability to change, vital in today’s dynamic business environment.
Adopting Kaizen in Business:
- Leadership Commitment: Top-level management must champion the Kaizen philosophy to create a culture of continuous improvement.
- Employee Training: Educate employees about Kaizen principles and methodologies, fostering a shared understanding.
- Establishing a Kaizen Team: Create a dedicated team responsible for driving and facilitating Kaizen initiatives.
- Identifying Areas for Improvement: Regularly assess processes and workflows to pinpoint areas requiring enhancement.
- Implementing Changes: Test and implement small-scale changes, gathering feedback and refining processes.
- Monitoring and Review: Continuously monitor the impact of changes, gather data, and assess the success of implemented improvements.
- Recognition and Rewards: Acknowledge and reward employees for their contributions, motivating them to actively participate in Kaizen initiatives.
Kaizen is not just a management strategy but a cultural shift toward continuous improvement. By embracing Kaizen, businesses can create a dynamic environment that fosters innovation, employee engagement, and sustained success in an ever-evolving marketplace. Through its principles of continuous improvement, empowerment, and waste reduction, Kaizen remains a powerful approach for businesses seeking long-term growth and competitiveness.
Image Credit: Image by rawpixel.com on Freepik